Science > AP®︎/College Chemistry > Molecular and ionic compound structure and properties > Bond hybridization Worked examples: Finding the hybridization of atoms in organic molecules Google Classroom About Transcript
Explain why the bond angles of a trigonal pyramidal molecule are smaller than those of a trigonal planar molecule? – Quora
Step by step Solved in 3 steps with 1 images SEE SOLUTION Check out a sample Q&A here Similar questions Im taking organic chemistry and in class we have to determine whether the moelcules are stable, unstable or impossible from looking at the lewis structure diagrams What steps do i take to determine their stability?
![C(sp2)–H···π(C≡N) interaction in [Ag+·Argentivorous molecule ⊃ acetonitrile] inclusion complexes - ScienceDirect](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0020169323002074-gr1.jpg)
Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
Example: sp 3 Hybridization in Methane; Because carbon plays such a significant role in organic chemistry, we will be using it as an example here. Carbon’s 2s and all three of its 2p orbitals hybridize to form four sp 3 orbitals. These orbitals then bond with four hydrogen atoms through sp 3-s orbital overlap, creating methane.The resulting shape is tetrahedral, since that minimizes electron
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
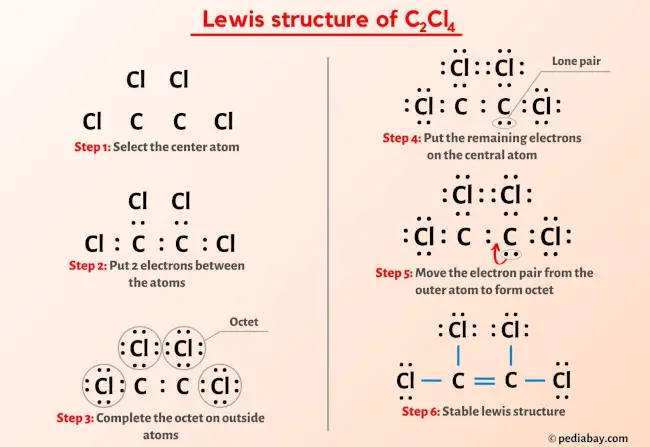
C2Cl4 Lewis Structure in 6 Steps (With Images) Hybridization. Hybridization is a simple model that deals with mixing orbitals to from new, hybridized, orbitals. This is part of the valence bond theory and helps explain bonds formed, the length of bonds, and bond energies; however, this does not explain molecular geometry very well. sp An example of this is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ).
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
What Is The Hybridization Of The C Atoms In C2cl4
Hybridization. Hybridization is a simple model that deals with mixing orbitals to from new, hybridized, orbitals. This is part of the valence bond theory and helps explain bonds formed, the length of bonds, and bond energies; however, this does not explain molecular geometry very well. sp An example of this is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ). Jun 23, 2023Now in the C2Cl4 molecule, you have to put the electron pairs between the carbon-carbon atoms and between the carbon-chlorine atoms. This indicates that these atoms are chemically bonded with each other in a C2Cl4 molecule. Step 4: Make the outer atoms stable. Place the remaining valence electrons pair on the central atom.
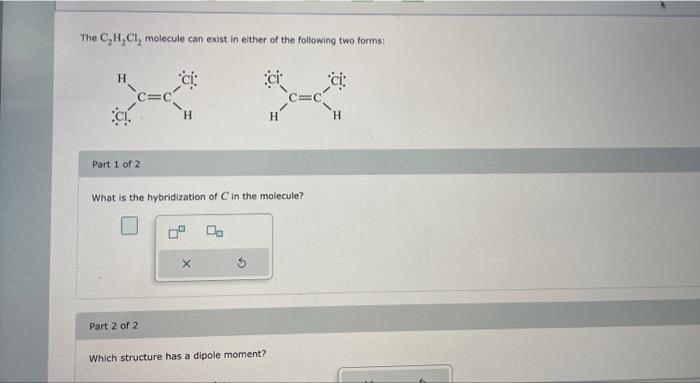
Solved The C2H2Cl2 molecule can exist in either of the | Chegg.com
Tools expand_more Help expand_more Get Help Feedback Readability x selected template will load here Error This action is not available. chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode Search Expand/collapse global hierarchy Home Bookshelves Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry I (Cortes) What is the expected bond angle between the central atom and any two adjacent chlorine atoms for the molecule C2Cl4? | Homework.Study.com

Source Image: homework.study.com
Download Image
Indicate the type of hybridization of each carbon atom in the following – YouTube Tools expand_more Help expand_more Get Help Feedback Readability x selected template will load here Error This action is not available. chrome_reader_mode Enter Reader Mode Search Expand/collapse global hierarchy Home Bookshelves Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry I (Cortes)

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Explain why the bond angles of a trigonal pyramidal molecule are smaller than those of a trigonal planar molecule? – Quora Science > AP®︎/College Chemistry > Molecular and ionic compound structure and properties > Bond hybridization Worked examples: Finding the hybridization of atoms in organic molecules Google Classroom About Transcript
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
C2Cl4 Lewis Structure in 6 Steps (With Images) Example: sp 3 Hybridization in Methane; Because carbon plays such a significant role in organic chemistry, we will be using it as an example here. Carbon’s 2s and all three of its 2p orbitals hybridize to form four sp 3 orbitals. These orbitals then bond with four hydrogen atoms through sp 3-s orbital overlap, creating methane.The resulting shape is tetrahedral, since that minimizes electron
Source Image: pediabay.com
Download Image
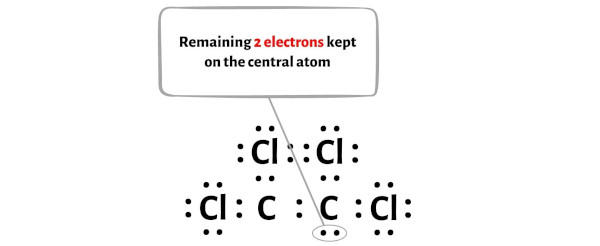
C2Cl4 Lewis Structure in 6 Steps (With Images) You can find the hybridization by AXE method; Here A represents the atom that we’re interested in (usually the central atom), X the number of atoms bonded to the central molecule or the one we’re interested in, and E are the non-bonding electrons (lone pairs). The total number of X and E is known as the steric number.
Source Image: pediabay.com
Download Image
Carbon atoms in C2(CN4) are: Hybridization. Hybridization is a simple model that deals with mixing orbitals to from new, hybridized, orbitals. This is part of the valence bond theory and helps explain bonds formed, the length of bonds, and bond energies; however, this does not explain molecular geometry very well. sp An example of this is acetylene (C 2 H 2 ).

Source Image: toppr.com
Download Image
The hybridisation of carbon atoms in C-C single bond of `HC-=C-CH=CH=CH_(2)` – YouTube Jun 23, 2023Now in the C2Cl4 molecule, you have to put the electron pairs between the carbon-carbon atoms and between the carbon-chlorine atoms. This indicates that these atoms are chemically bonded with each other in a C2Cl4 molecule. Step 4: Make the outer atoms stable. Place the remaining valence electrons pair on the central atom.

Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Indicate the type of hybridization of each carbon atom in the following – YouTube
The hybridisation of carbon atoms in C-C single bond of `HC-=C-CH=CH=CH_(2)` – YouTube Step by step Solved in 3 steps with 1 images SEE SOLUTION Check out a sample Q&A here Similar questions Im taking organic chemistry and in class we have to determine whether the moelcules are stable, unstable or impossible from looking at the lewis structure diagrams What steps do i take to determine their stability?
C2Cl4 Lewis Structure in 6 Steps (With Images) Carbon atoms in C2(CN4) are: You can find the hybridization by AXE method; Here A represents the atom that we’re interested in (usually the central atom), X the number of atoms bonded to the central molecule or the one we’re interested in, and E are the non-bonding electrons (lone pairs). The total number of X and E is known as the steric number.