Ionic bonds can be observed on the solids at room temperature which have high melting points. Ionic bond is stronger than covalent bond, however, other compounds demonstrate different properties of the bond due to various factors, such as environmental conditions, electronegativity, bond energy, orbitals, etc. Share.
Are covalent network solids stronger than ionic bonds in regards to intermolecular forces? – Quora
Figure 1. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as they approach each other, and the single electrons on each atom are shared to form a covalent bond. The bond length is the internuclear distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved.

Source Image: chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Download Image
Bond Strength: Covalent Bonds Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy (see [link] ).
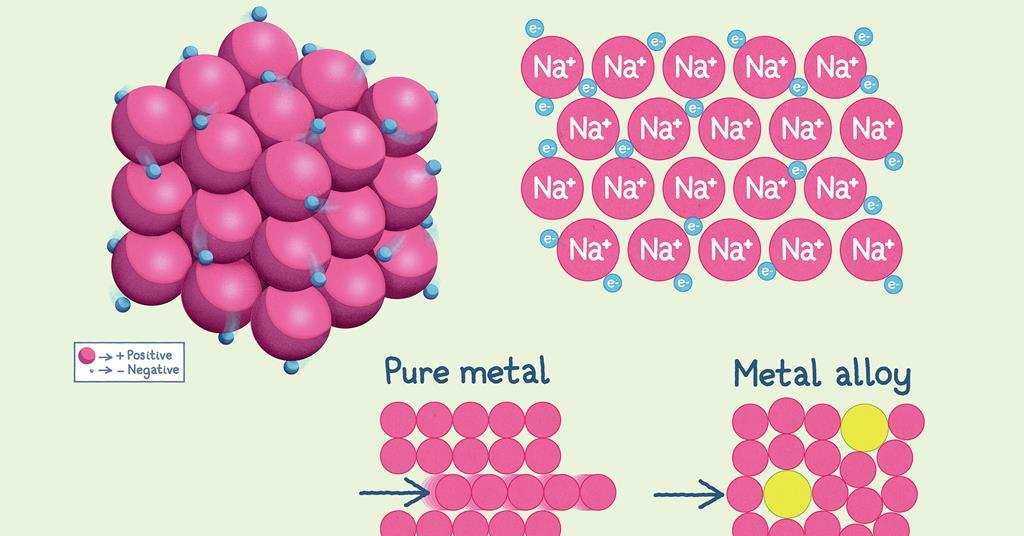
Source Image: edu.rsc.org
Download Image
Achievers Dream – Chemical Bonding Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds; Ionic compounds tend to be a solid with a definite shape at room temperature, covalent compounds are usually gases, liquids or soft solids; Ionic compounds often do not dissolve in organic solvents, while covalent compounds often do; We hope that gives you a better sense of ionic vs covalent.

Source Image: in.pinterest.com
Download Image
Is A Covalent Bond Stronger Than An Ionic Bond
Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds; Ionic compounds tend to be a solid with a definite shape at room temperature, covalent compounds are usually gases, liquids or soft solids; Ionic compounds often do not dissolve in organic solvents, while covalent compounds often do; We hope that gives you a better sense of ionic vs covalent. There are a variety of ways atoms bond to one another. Some bonds are weaker, and some are stronger. Two of the strongest forms of chemical bond are the ionic and the covalent bonds. Chemical bonds form between two atoms, each with its own electron environment. If each of the two atoms shares an electron with the other atom nearly equally, the
Ionic vs. Covalent Bond – What’s The Difference (With Table) | Diffzy | Covalent bonding, Ionic bonding, Ionic and covalent bonds
The stronger a bond, the greater the energy required to break it. The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. The bond energy for a diatomic molecule, D X-Y, is defined as the standard enthalpy change for the endothermic reaction: Ionic vs covalent vs metallic bonds … | Teaching chemistry, Chemistry education, Chemistry basics

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Ionic Bond: Electrovalent Bond, Definition, Formation & Examples The stronger a bond, the greater the energy required to break it. The energy required to break a specific covalent bond in one mole of gaseous molecules is called the bond energy or the bond dissociation energy. The bond energy for a diatomic molecule, D X-Y, is defined as the standard enthalpy change for the endothermic reaction:

Source Image: geeksforgeeks.org
Download Image
Are covalent network solids stronger than ionic bonds in regards to intermolecular forces? – Quora Ionic bonds can be observed on the solids at room temperature which have high melting points. Ionic bond is stronger than covalent bond, however, other compounds demonstrate different properties of the bond due to various factors, such as environmental conditions, electronegativity, bond energy, orbitals, etc. Share.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Achievers Dream – Chemical Bonding Bond Strength: Covalent Bonds Stable molecules exist because covalent bonds hold the atoms together. We measure the strength of a covalent bond by the energy required to break it, that is, the energy necessary to separate the bonded atoms. Separating any pair of bonded atoms requires energy (see [link] ).

Source Image: achieversdream.com.sg
Download Image
Predicting Bond Type Between Elements Based on Ionization Energy | Chemistry | Study.com The two main types of chemical bonds are ionic and covalent bonds. An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond, while electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms. The only pure covalent bonds occur between identical atoms. Usually, there is some polarity (polar covalent bond

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Chemistry lovers added a new photo —… – Chemistry lovers Ionic bonds are much stronger than covalent bonds; Ionic compounds tend to be a solid with a definite shape at room temperature, covalent compounds are usually gases, liquids or soft solids; Ionic compounds often do not dissolve in organic solvents, while covalent compounds often do; We hope that gives you a better sense of ionic vs covalent.

Source Image: facebook.com
Download Image
Difference Between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds | Definition, Formation, Properties | Covalent bonding, Chemistry education, Ionic bonding There are a variety of ways atoms bond to one another. Some bonds are weaker, and some are stronger. Two of the strongest forms of chemical bond are the ionic and the covalent bonds. Chemical bonds form between two atoms, each with its own electron environment. If each of the two atoms shares an electron with the other atom nearly equally, the

Source Image: pinterest.com
Download Image
Ionic Bond: Electrovalent Bond, Definition, Formation & Examples
Difference Between Ionic Covalent and Metallic Bonds | Definition, Formation, Properties | Covalent bonding, Chemistry education, Ionic bonding Figure 1. The potential energy of two separate hydrogen atoms (right) decreases as they approach each other, and the single electrons on each atom are shared to form a covalent bond. The bond length is the internuclear distance at which the lowest potential energy is achieved.
Achievers Dream – Chemical Bonding Chemistry lovers added a new photo —… – Chemistry lovers The two main types of chemical bonds are ionic and covalent bonds. An ionic bond essentially donates an electron to the other atom participating in the bond, while electrons in a covalent bond are shared equally between the atoms. The only pure covalent bonds occur between identical atoms. Usually, there is some polarity (polar covalent bond